

Module 2: Prompt Engineering for Legal Analysis Lesson 2.1 – Structuring Clear and Effective Legal Prompts
Module 2: Prompt Engineering for Legal Analysis
Lesson 2.1 – Structuring Clear and Effective Legal Prompts
Learning Objectives
- Explain what a prompt is and how prompt quality affects AI output.
- Apply structured prompt formats appropriate for legal reasoning and document drafting.
- Use context, task directives, and constraints to guide AI responses precisely.
- Identify and correct vague or ambiguous prompts to prevent inaccurate or broad responses.
- Begin developing reusable legal prompting frameworks for everyday practice.
AI works by predicting language patterns based on the instructions it receives.
The clearer, more structured, and more specific the prompt, the more reliable and relevant the AI’s response will be.
This lesson focuses on how to write prompts that produce clear, accurate, legally-useful outputs.
1. What Is a Prompt?
A prompt is the instruction or input you provide to the AI to generate a response.
Prompts may include:
- Background information
- Legal issues
- Facts
- The task to be performed
- Required formatting
A prompt is not a question — it is a directive.
2. Why Prompt Structure Matters
AI does not understand legal reasoning. It responds based on language prediction.
Therefore:
- Vague input → vague output
- Broad input → broad output
- Precise input → precise output
The lawyer’s task is to frame the issue clearly, just as in legal writing.
3. The Four Elements of an Effective Legal Prompt

Example Prompt Format:
Context: [Describe relevant facts or legal issue]
Task: [What you want the AI to produce]
Constraints: [Include jurisdiction, tone, scope, etc.]
Format: [Specify bullet points, outline, paragraphs, etc.]
4. Example – Weak vs. Strong Legal Prompts
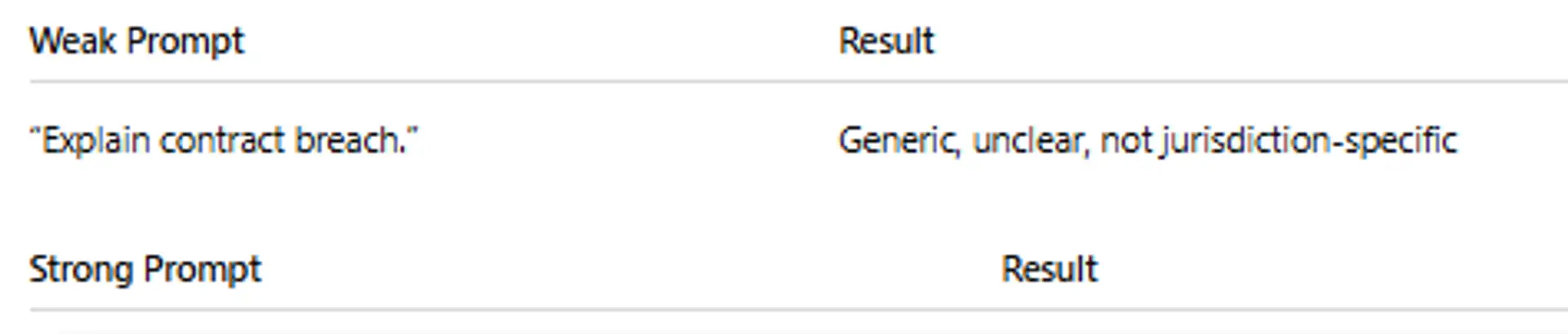
Context: A service contract governed by Massachusetts law.
Task: Provide a clear explanation of what constitutes a material breach.
Constraints: Focus on elements required to prove breach in civil litigation.
Format: 4 bullet points, concise.
Produces a clear, jurisdiction-appropriate, structured explanation.
5. Applying Prompt Structure to Legal Analysis
Example Scenario: Client claims landlord failed to make necessary repairs.
Effective Prompt:
Context: Tenant alleges landlord did not repair plumbing issues after written notice. Jurisdiction: California.
Task: Identify potential legal claims available to the tenant.
Constraints: Reference statutory or regulatory obligations where applicable. Do not create case citations. Keep language clear.
Format: List claims with brief explanation below each.
This leads to relevant, issue-specific legal analysis, not general landlord-tenant law theory.
6. Prompting for Drafting (Letters, Memos, Arguments)
Drafting Prompt Template:
Context: [Case situation, facts, party roles]
Task: Draft [memo/letter/argument paragraph/etc.]
Constraints: Tone must be professional and neutral; do not assert conclusions without stating reasons.
Format: [Desired structure, such as IRAC, CREAC, bullet outline, etc.]
7. Prompting for Case Summaries
Context: Summarize the following case text.
Task: Provide a structured summary.
Constraints: Include (1) facts, (2) procedural posture, (3) issue, (4) holding, (5) reasoning.
Format: Use numbered sections.
Case Summary Prompt Template:
This reinforces legal reasoning structure.
8. Common Prompting Errors to Avoid

9. Practical Exercise (Recommended Practice)
Try rewriting this vague prompt:
“Help me write a demand letter.”
Using the structure learned:
Context: Client paid contractor $8,500 for renovation. Contractor did not perform work. Jurisdiction: Illinois.
Task: Draft a firm but professional demand letter requesting refund or performance.
Constraints: Do not include threats, legal conclusions, or citations.
Format: 4 short paragraphs: introduction, issue, requested action, deadline.
10.Supplementary Learning Resource
Video:
- How to Write Perfect AI Prompts in 2025 (Complete Guide)
- Master the Perfect ChatGPT Prompt Formula (in just 8 minutes)!
- The ULTIMATE 2025 Guide to Prompt Engineering - Master the Perfect Prompt Formula!
Lesson 2.1 Quiz
Structuring Clear and Effective Legal Prompts
Please complete this quiz to check your understanding of Lesson 2.1. You must score at least 70% to pass this lesson quiz. This quiz counts toward your final certification progress.
Click here for Quiz 2.1
Conclusion
Effective legal prompting is a matter of clarity, specificity, and structure. When the lawyer frames context, defines the task, applies constraints, and selects a format, AI can provide accurate, useful, and efficient support. Prompting is an applied skill that strengthens with practice, and it forms the foundation for advanced AI-assisted legal work in subsequent lessons.
Next and Previous Lesson
Lesson 2.2: Multi-Step Reasoning Prompts for Legal Argument
Previous:Lesson 1.3 – Ethical Use of AI in Legal Practice
Related Posts
© 2025 Invastor. All Rights Reserved

User Comments