

Module 1: Foundations of Legal AI and ChatGPT Lesson 1.2 — Understanding ChatGPT and Legal Use Cases
Module 1: Foundations of AI in Legal Practice
Lesson 1.2 – Appropriate and Inappropriate Uses of ChatGPT in Legal Work
Learning Objectives
- By the end of this lesson, the learner should be able to:
- Identify specific legal tasks where ChatGPT can be used effectively.
- Recognize tasks where AI assistance requires attorney oversight.
- Distinguish situations where ChatGPT should not be used due to confidentiality or ethical concerns.
- Apply structured prompts that reduce errors and improve AI output quality.
- Verify AI-generated content to ensure accuracy and legal reliability.
- Ensure compliance with ethical obligations when using AI in legal work.
- Understand the difference between drafting support and legal reasoning, and who is responsible for both.
- Implement firm or personal guidelines for safe and responsible AI use.
This lesson clarifies where ChatGPT can safely fit into legal workflows, where it poses risk, and what safeguards lawyers must maintain to ensure accuracy, confidentiality, and compliance with professional duties.
1.Effective Uses of ChatGPT in Law Practice
ChatGPT can support tasks that require drafting, summarizing, explaining, and organizing information, such as:
- Drafting first-version memos, letters, agreements, summaries, and outlines
- Summarizing lengthy documents and discovery data
- Converting complex legal language into plain language for clients
- Structuring research approaches and identifying key issues
- Supporting administrative procedures and office workflows
2.Tasks That Require Caution
ChatGPT can assist in analysis structure, but lawyers must verify and complete the reasoning. Caution is required when:
- Identifying controlling legal authority
- Applying legal standards to case-specific facts
- Preparing documents for court submission
3.Tasks That Should Not Be Performed Using Public ChatGPT
Public or unsecured AI platforms should not be used to input:
- Client names
- Case numbers
- Privileged facts
- Confidential commercial or personal information
- Only secure, law-compliant AI environments should be used for confidential matters.
4.Why Verification Is Essential
ChatGPT does not retrieve real-time law and may generate:
- Outdated or misinterpreted authority
- Incorrect legal principles
- Completely fabricated case citations
Lawyers must verify all legal statements through official sources (LexisNexis, Westlaw, Bloomberg Law, etc.).
5.The Lawyer Remains the Decision-Maker
- AI supports drafting and organization, but:
- Strategic decisions
- Legal interpretation
- Client advice
- Final document preparation
Must always be performed by the lawyer.
6.Risk Level and Oversight Guide
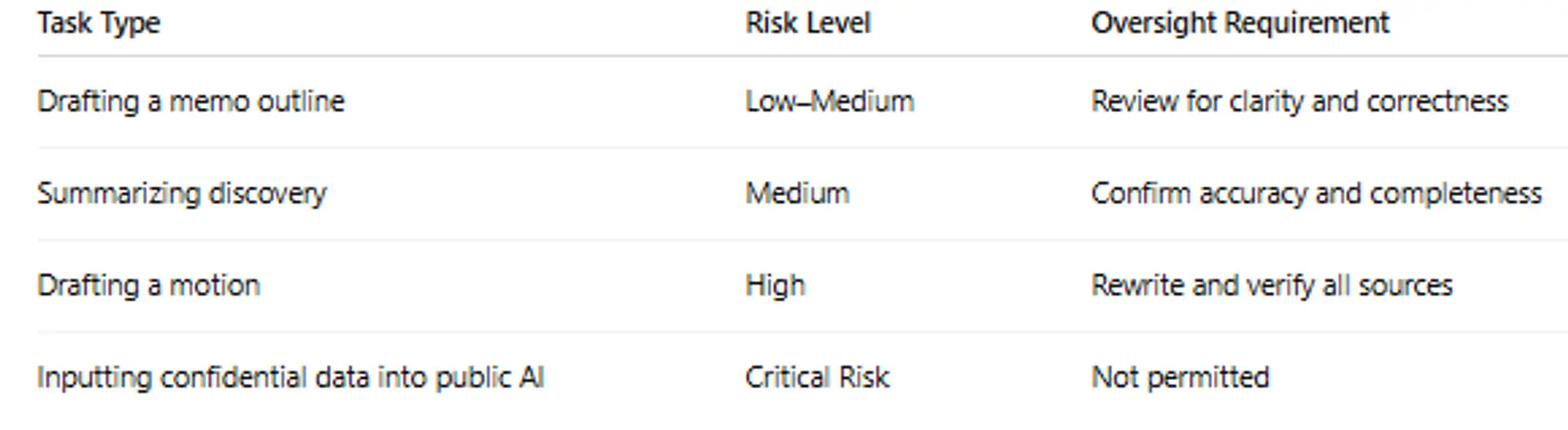
7.Prompt Structure for Reliable Results
Role + Task + Constraints reduces errors and improves output quality.
Example:
“You are assisting as a legal writing intern. Summarize the following discovery transcript into a neutral, factual overview. Limit to 400 words. Do not infer legal conclusions.”
8.Firm and Personal Policy Guidelines
Effective AI governance includes:
- Attorney review required for all AI-generated work
- Verification of all legal authority
- Use of secure platforms only
- Documentation of when and how AI was used
9.Supplementary Learning Resource
Video:
- How to Use ChatGPT to Ruin Your Legal Career
- How To Use ChatGPT Prompts for Lawyers
- How AI Impacts the Practice of Law
Lesson Quiz 1.2
Please complete this quiz to check your understanding of the lesson. You must score at least 70% to pass this lesson quiz. This quiz counts toward your final certification progress.
Answer the quiz using the Google Form below.
Conclusion
ChatGPT is a powerful tool for improving efficiency in legal practice when used responsibly. It can accelerate drafting, research organization, explanation, and workflow—but it cannot replace legal reasoning, professional accountability, or confidentiality obligations. The lawyer must always review, verify, and finalize the results.
Next and Previous Lesson
Next - Lesson 1.3: Understanding ChatGPT and Legal Use Cases
Previous - Lesson 1.1: What AI Is and How It Works in Legal Contexts
Related Posts
© 2025 Invastor. All Rights Reserved

User Comments