
How Can You Treat Swelling of Deeper Skin Layers?
Swelling of the deeper layers of skin can be alarming, uncomfortable, and sometimes dangerous. This type of swelling often involves inflammation beneath the surface, in tissues like the dermis, subcutaneous fat, or fascia. While minor cases may resolve with self care, others require prompt medical attention and, in certain cases, prescription antibiotics such as cephalexin capsules.
This guide explores the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive steps for swelling in deeper skin layers, with a focus on when cephalexin capsules might be appropriate.
Understanding Swelling of Deeper Skin Layers
Medically, swelling in the deeper skin layers is often referred to as cellulitis or deep dermal inflammation. It can also be part of other conditions like
Erysipelas a superficial form of skin infection.
Abscesses localized pockets of pus beneath the skin.
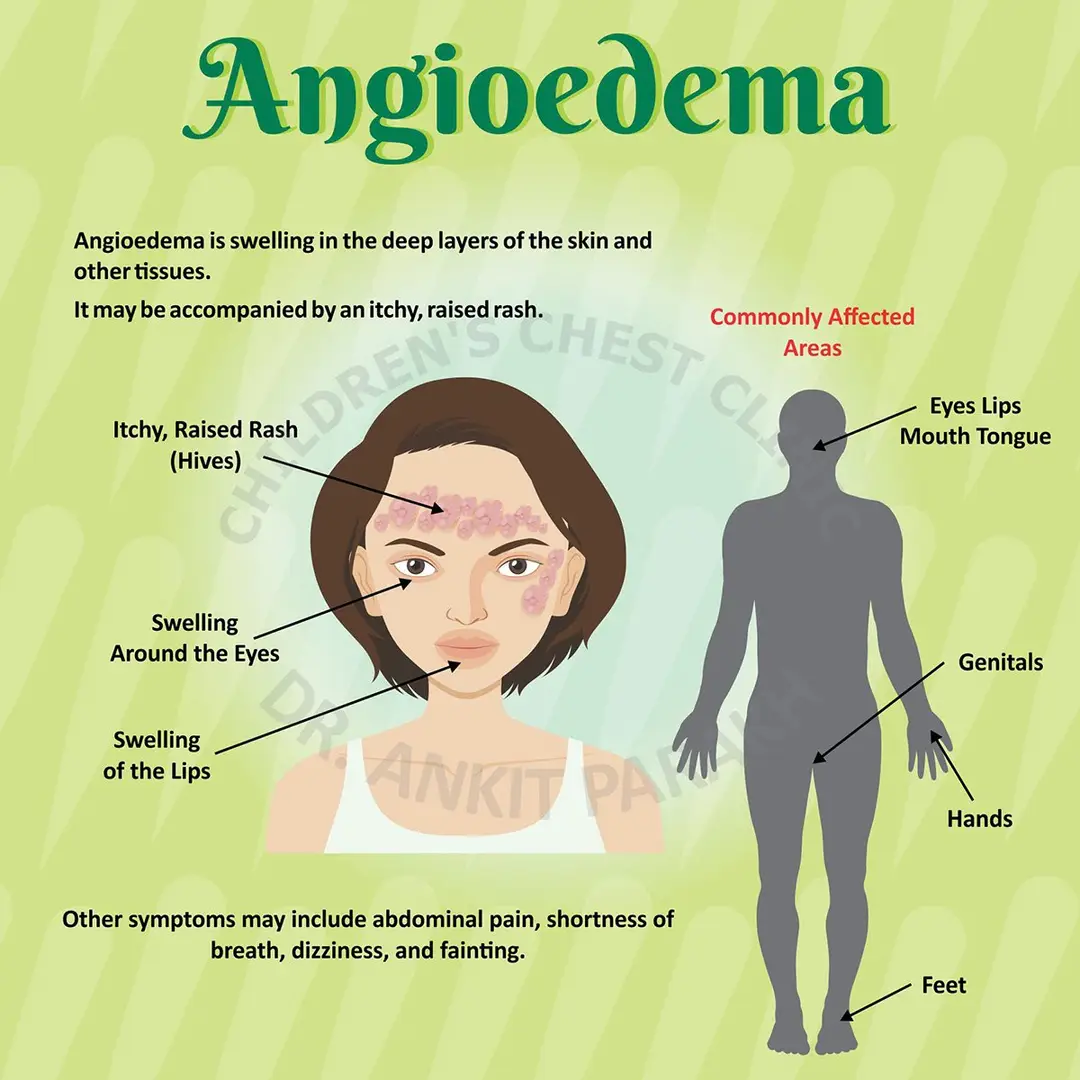
Allergic angioedema sudden swelling due to allergic reaction.
Insect bite reactions which can penetrate deeper layers.
These conditions may be caused by bacterial infection, allergic reaction, trauma, or an underlying systemic problem. Infections are most commonly due to Streptococcus or Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, both of which can penetrate through small cuts or cracks in the skin.
Common Symptoms
When swelling affects deeper skin layers, you may notice
Redness and warmth over the area.
Pain or tenderness that increases with pressure.
Firmness in the affected skin.
Fever or chills in more severe cases.
Rapid expansion of the swollen area.
If you see red streaks, experience spreading swelling, or develop a fever, you should seek urgent medical care these can be signs of a serious infection that may require antibiotics such as cephalexin capsules.
Why Infections Need Prompt Treatment
The deeper the infection, the greater the risk of complications like
Abscess formation requiring drainage.
Sepsis a life threatening bloodstream infection.
Tissue necrosis destruction of healthy tissue.
Spread to muscles, joints, or bones potentially leading to long-term disability.
Prompt treatment prevents these outcomes, reduces pain, and promotes faster recovery.
Medical Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of swelling.
- Antibiotic Therapy
- If a bacterial infection is suspected, doctors may prescribe antibiotics. Cephalexin capsules are a common choice, particularly for skin and soft tissue infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
Cephalexin Capsules Overview
Type: First generation cephalosporin antibiotic.
Mechanism: Disrupts bacterial cell wall formation, leading to bacterial death.
Typical Uses: Cellulitis, wound infections, and some abscesses.
Dosage: Often prescribed 2-4 times daily, depending on severity and patient factors.
(Only a doctor can determine the correct dose.)
Cephalexin capsules are effective against many strains of Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus. However, they are not effective against MRSA, so your doctor may choose a different antibiotic if MRSA is suspected.
- Supportive Measures
- In addition to antibiotics like cephalexin capsules, supportive measures help reduce swelling and discomfort
Elevation of the affected limb to improve fluid drainage.
Warm compresses to promote blood flow and healing.
Hydration to support immune response.
Over-the-counter pain relief (e.g., acetaminophen or ibuprofen), if approved by your doctor.
- Allergic or Non-Infectious Swelling
- If the swelling is caused by an allergic reaction rather than infection, antibiotics like cephalexin capsules will not help. Instead, treatment may involve
Antihistamines (oral or topical).
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
Avoidance of the triggering allergen.
- Surgical or Procedural Intervention
- Some deep skin infections develop abscesses. These require incision and drainage in addition to antibiotics. Cephalexin capsules may be given afterward to clear remaining bacteria and prevent recurrence.
Home Care for Mild Cases
While serious cases require medical care, mild swelling due to minor injury or irritation may respond to:
Resting the affected area.
Gentle cleansing with mild soap and water.
Applying an antibacterial ointment.
Monitoring closely for signs of infection.
If you notice any worsening or spreading redness, seek medical care immediately.
When to Seek Urgent Care
Contact a healthcare provider right away if you experience
Rapidly spreading redness and swelling.
Severe pain.
High fever or chills.
Pus or unusual drainage.
Numbness or loss of function.
These symptoms may indicate an aggressive infection requiring antibiotics such as cephalexin capsules or intravenous therapy.
Preventing Deep Skin Layer Swelling
Prevention focuses on skin protection and early treatment of minor wounds
Maintain good hygiene Regular handwashing reduces bacterial spread.
Moisturize skin Prevents cracks that allow bacteria entry.
Treat cuts promptly Clean and cover even small wounds.
Manage chronic conditions Diabetes and poor circulation increase infection risk.
Wear protective clothing Especially in environments where cuts or insect bites are likely.
Possible Side Effects of Cephalexin Capsules
Like all medications, cephalexin capsules may cause side effects, including
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Abdominal discomfort.
Allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling of face/tongue).
Rarely, severe allergic responses like anaphylaxis.
If you experience trouble breathing, severe rash, or swelling of the throat after taking cephalexin capsules, seek emergency care immediately.
Drug Interactions and Cautions
Before starting cephalexin capsules, inform your doctor if you
Are allergic to penicillin or other cephalosporins.
Have kidney disease.
Are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Take other medications that may interact with antibiotics.
The Importance of Completing the Full Course
One of the most important principles in antibiotic therapy is finishing the entire prescribed course of cephalexin capsules, even if you feel better after a few doses. Stopping early can allow bacteria to survive, potentially leading to recurrence or antibiotic resistance.
Final Thoughts
Swelling of deeper skin layers can be caused by infection, allergy, trauma, or other factors. Correct treatment depends on identifying the underlying cause. Bacterial infections often respond well to antibiotics such as cephalexin capsules, especially when started promptly and combined with supportive care.
However, because deeper skin swelling can sometimes signal a severe, fast-moving infection, it’s important to avoid self-diagnosis. Always consult a healthcare provider to determine the safest and most effective treatment for your specific situation.
By recognizing symptoms early, seeking prompt care, and following medical advice including proper use of cephalexin capsules when indicated you can reduce complications, speed recovery, and protect your long-term health.
Related Posts
© 2025 Invastor. All Rights Reserved

User Comments